A Guide to IM Business Models
The Internet offers many IM business models for generating income through online marketing, selling digital products, delivering services virtually, and more. This comprehensive guide covers ten key internet marketing (IM) business models along with examples, pros and cons, and tips for getting started with each.

1. Affiliate Marketing: IM Business Models
Affiliate marketing involves promoting third-party products or services on your website, social media, or other digital assets. Whenever someone clicks your specialized tracking link and completes a desired action, like making a purchase, you earn a commission.
**Examples**
– Promoting products on your blog
– Sharing affiliate coupon codes on Instagram
– Reviewing services on YouTube
**Pros**
– Little upfront investment – Mostly your time
– Wide range of products/services to promote
– Leverage platforms like affiliate networks
– Completely online-based
**Cons**
– Payout rates vary – Some commissions are small
– Must build sufficient traffic to earn significant income
– Reliant on consistent promotion and content creation
– Potentially saturated markets
**Tips to Start**
– Join affiliate programs like Amazon Associates, ShareASale, Clickbank
– Research high-commission, in-demand niches
– Create a website or social media account focused on niche
– Review products and share affiliate links
2. Selling Digital Products: IM Business Models
This model involves creating value-adding digital products like ebooks, courses, membership sites, or software tools and selling direct access. Products provide utility for buyers versus a passive affiliate promotion.
**Examples**
– Online cooking course
– Financial planning ebook
– Membership site for yoga tutorial videos
– Budgeting spreadsheet template
**Pros**
– Higher profit margins by selling your own creations
– Recurring passive income potential
– Scales through automation
– Builds personal brand and authority
**Cons**
– Requires initial time and monetary investment to create products and site
– Need expertise in a niche to develop valuable products
– Marketing efforts essential for sufficient product discoverability
**Tips to Start**
– Identify audience needs through market research
– Choose a niche where you can provide solutions as digital products
– Develop lead magnets like free checklists to build an email list
– Create first simple but useful product like a how-to guide
3. Dropshipping: IM Business Models
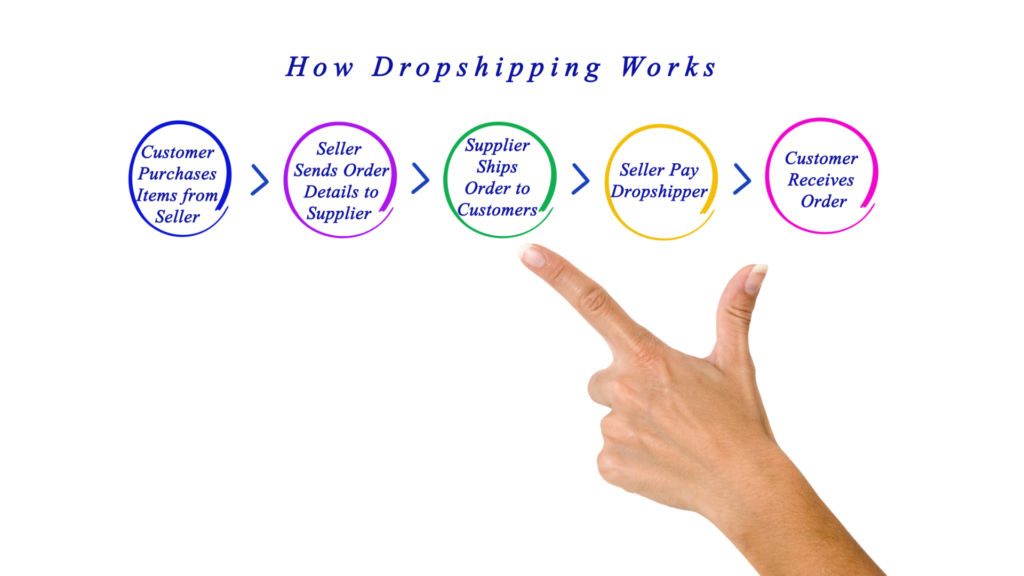
Dropshipping involves setting up an online store selling products shipped directly from a wholesale supplier to customers, bypassing inventory/handling on your end. You keep a profit margin between retail and wholesale costs.
**Examples**
– Pet supply shop dropshipping treats and toys
– Home goods store selling dropshipped kitchenware
– Fashion outlet dropshipping designer merchandise
**Pros**
– Minimal startup costs – Mostly web hosting and theme
– Don’t need to buy and hold product inventory
– Wide selection of suppliers and products to sell
– New automation technology streamlines workflow
**Cons**
– Low profit margins on competitive products
– Reliant on supplier for order fulfillment and quality
– Requires significant marketing to drive steady sales
– Customer service effort required
**Tips to Start**
– Source reputable suppliers through directories like SaleHoo
– Choose niche products with higher margins
– Create a brand logo and professional site
– Market aggressively through paid and social advertising
4. Retail Arbitrage: IM Business Models
Retail arbitrage involves identifying products priced low from one retail source, purchasing them, then reselling them on a marketplace like Amazon or eBay for a higher price. You keep the price difference as profit.
**Examples**
– Buying clearance electronics from Target and then selling on eBay
– Purchasing discounted apparel from TJ Maxx and reselling on Poshmark
– Getting heavily reduced toys from Walmart and then listing them on Amazon
**Pros**
– Allows buying products below market value
– Don’t need your own website or branding
– Can start small and scale up
– Leverage marketplaces like Amazon for exposure
**Cons**
– Requires time to source discounted products
– Need to buy inventory upfront without guaranteed sales
– Processing, photographing, and listing items takes effort
– Storage space needed for unsold goods
**Tips to Get Started**
– Use apps like ShopSavvy to identify discounted retail items
– Compare prices across marketplaces to identify resell opportunities
– Focus on light, inexpensive products to transport and store easily
– List immediately before seasonal demand decreases
Need More IM Business Models?
High Ticket Digital Marketing- The 411
Just exactly What is an Affiliate marketing Program?
Affiliate Marketing Keywords: 8 HOT Tips
5. Selling Services: IM Business Models
This model involves offering your professional services online, like consulting, graphic design, writing, development, marketing, and more. Clients hire and pay you for your expertise.
**Examples**
– Video editing and animation
– Business strategy consulting
– Social media management
– Logo and branding design
– Bookkeeping services
**Pros**
– Monetize existing skills and talents
– Very low start-up costs – just initial marketing
– Flexible to operate from anywhere
– Scales through raising rates and delegation
**Cons**
– Inconsistent income depending on the number of clients
– Time intensive with active work required for each project
– Need to be disciplined when self-employed
– Getting initial clients requires hustle
**Tips to Get Started**
– Specify the services you will offer based on your expertise
– Set rates in line with industry benchmarks
– Build a portfolio site to showcase work samples
– Promote through social platforms like LinkedIn
6. Freelance Writing: IM Business Models
Like general consulting services, freelance writing involves creating and selling written content to clients. This leverages writing abilities specifically. Clients may include brands, agencies, publishers, individuals, etc.
**Examples**
– Blog, website, and social media posts
– Press releases, articles, and other PR services
– Whitepapers, ebooks, guides, and other long-form pieces
– Creative writing – stories, poems, lyrics, scripts
**Pros**
– Accessible way to begin monetizing writing skills
– Work from anywhere with just a laptop and internet
– Choose your own workload – go part or full-time
– Broad client opportunities – brands, publishers, individuals
**Cons**
– Income fluctuates based on the number of clients
– Deadlines require strong time management skills
– Pitching services to new clients can be intimidating
– Writing expertise key – not just a love of writing
**Tips to Get Started**
– Determine writing niches and services to offer clients
– Build a portfolio of sample writings in your niche
– Create writer’s website to showcase abilities
– Reach out to potential clients pitching services
7. Ad Revenue Sites: IM Business Models
This model involves creating websites primarily aimed at generating income through advertisements like display ads, sponsored posts, contextual ads, and influencer marketing. Traffic volume is the key revenue driver.
**Examples**
– Parenting blog earning CPM ad revenue
– Pet care site monetized with Petco display ads
– Tech review site selling sponsored contributor posts
**Pros**
– Very scalable – earn per view versus per sale
– No inventory or fulfillment is required
– Offers passive income once site traffic is established
– Need site creation skills – no specific niche expertise
**Cons**
– Considerable traffic volume needed to earn well
– Potential saturation of ad-based sites
– Requires fresh, continually updated content
– Ad blockers impact earnings
**Tips to Get Started**
– Choose a popular niche and research related keywords
– Install Google AdSense to serve context-based ads
– Focus on search-friendly content creation and SEO
– Leverage influencers and sponsored posts once established
8. Membership Sites: IM Business Models
This model involves users paying a recurring subscription fee to access gated, exclusive content on a membership site. Content is only available to paying members.
**Examples**
– Virtual fitness classes and workout videos
– Premium investing tips and stock picks
– Online coding course library
– Archive of meditation and mindfulness content
**Pros**
– Can offer high-value, premium content to subscribers
– Recurring revenue through automatic membership renewals
– Positioned as exclusive, establishing desire
– Acquiring users has cost – but focus shifts to retention
**Cons**
– Requires extensive, high-quality content creation
– Must continually add new content to retain users
– Promotion needed to gain initial subscribers
– Added complexity of access control and drip content
**Tips to Get Started**
– Determine the premium offering subscribers will pay for
– Software like MemberPress simplifies the creation
– Gate some existing free content to entice potential members
– Offer tiered plans – introductory > premium > elite
9. Info Products: IM Business Models
This model focuses on packaged information products like ebooks, online courses, templated documents, cheat sheets, etc. Users pay for digitally delivered, immediately downloadable content.
**Examples**
– Yoga training video course
– Meal planning ebook with recipes and shopping lists
– Social media image templates and graphics
– Beginner online course on interior design
**Pros**
– Higher profit margins selling your own creations
– Buyer accessible – no physical shipments
– Can reuse content or repurpose from blog
– Establish yourself as an authority through products
**Cons**
– Requires some expertise in niche for quality content
– Creation and marketing efforts key to discoverability
– Potential audience doubts about intangible digital products
– Requires persuading people to pay upfront
**Tips to Get Started**
– Identify audience needs through surveys, interviews, research
– Offer a free lead magnet-like checklist to build an email list
– Develop a simple yet useful first product like a how-to guide
– Expand into the membership model for ongoing access
10. Software as a Service (SaaS): IM Business Models
This model involves creating specialized software, apps, or other digital tools that solve specific user pain points and then selling access on a subscription basis.
**Examples**
– Project management software
– Health and fitness app
– Grammar checking tool
– Password manager software
**Pros**
– Monthly recurring revenue from ongoing subscriptions
– High value for users drives willingness to pay
– Can scale to thousands of users with low incremental cost
– Establishes brand and authority in your software niche
**Cons**
– High upfront investment of time and money to develop
– Very technical – requires software development skills
– Promotion and user acquisition costs can be high
– Ongoing customer support burden
**Tips to Get Started**
– Survey potential users to affirm demand for a software concept
– Calculate total addressable market (TAM) to gauge revenue potential
– Develop a basic MVP app with stripped-down features
– Offer time-limited free trials to hook users before charging
The opportunities to build lucrative online businesses are plentiful thanks to diverse monetization models. By matching your skills and interests with the right IM business model; you can establish a successful commercial venture. Conduct market research, develop your expertise, and dive in!